Mechanical Vapor Recompression (MVRE)
Mechanical Vapor Recompression (MVRE) is an energy recovery operation which can be used to recycle waste heat (Latent Heat) to improve energy efficiency.

Process Description :-
Mechanical vapor recompression is the advance and efficient way of the evaporation method to achieve zero-liquid discharge for any type of industrial effluent.
Prior to start evaporation process first cooling water circulation is started and generation of appropriate vacuum is being maintain by the vacuum pump, the purpose of the vacuum is to lower down the boiling point of the solution.
In MVRE, feed liquid enters at the top of calandria from the feed tank via feed pump through Pre-Heater.
Preheaters are used to exchange the sensible heat of condensate water generated during evaporation process to increase the initial temperature of the incoming feed, simultaneously decreasing the temperature of the condensate water which leads to decrease in the total energy requirement for the entire system.
After reaching minimum level of the effluent in the bottom part of the calandria, recirculation pumps start.
The Liquid is evenly distributed into the tubes via a distributor plate and gradually moves downward by gravity forming the film on the inner surface of the tubes.
To start the evaporation process external steam is being provided to the shell side of the calandria for heating of the tubes.
Due to conductive heat transfer, steam passes its latent heat to effluent and evaporation takes place. A water-vapor mixture is being generated which goes to Vapor-Liquid Separator called VLS.
While the concentrated liquid is recirculated in the Calandria by a recirculation pump.
In VLS, vapor is separated from water vapor mixture by means of gravity.
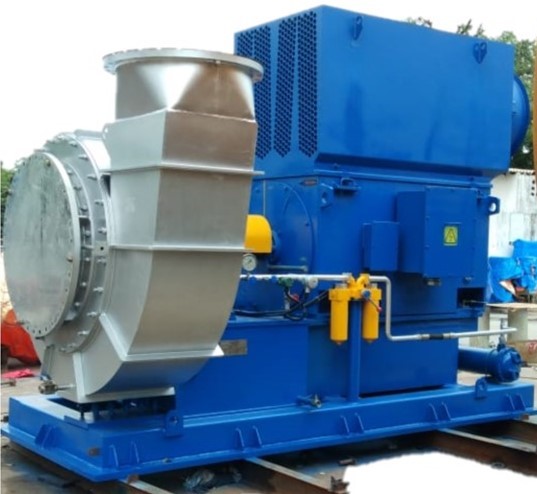
Now the pure water vapor from VLS, will be sucked by MVRE Fan/Blower.
Mechanical energy is added to incoming vapor by volumetric compression which leads to increase in the pressure & temp. of the incoming vapor. And thus, raising the enthalpy of the vapor to desire level
These vapor with high temp. and pre. And enthalpy has sufficient energy and ready to transfer its latent heat to the feed inside the tube. And thus no need of further steam is required. this cycle continuous which leads to no need of continuous steam during the continuous operation.
From the bottom of the calandria, reject of the MVRE at a certain concentration, goes to ATFD for final solid liquid separation, and thus achieving true mean of Zero Liquid Discharge.
Advantages :-
- Low Steam Consumption.
- Low Operating Cost
- Operates on a small temperature difference.
Application :-
- Zero Liquid Discharge
- Waste water treatment
- Salt recovery
- Caustic recovery
- Product concentration