DAF (Dissolve air flotation)
DAF is an unit Process for treatment of WTP/WWTP. DAF - Dissolved air flotation is a separator that clarifies wastewaters (or other waters) by the removal of suspended matter such as emulsified oil or solids. The removal is achieved by dissolving air in the water or wastewater under pressure and then releasing the air at atmospheric pressure in a flotation tank or basin. The released air forms tiny bubbles which adhere to the suspended matter causing the suspended matter to float to the surface of the water where it may then be removed by a skimming device.
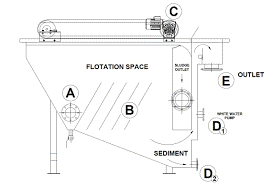
Process Description :-
The feed water to the DAF float tank is often (but not always) dosed with a coagulant to coagulate the colloidal particles and/or a flocculants to conglomerate the particles into bigger clusters. A portion of the clarified effluent water leaving the DAF tank is pumped into a small pressure vessel (called the Air Saturation Vessel) into which compressed air is also introduced. This results in saturating the pressurized effluent water with air. The air-saturated water stream is recycled to the inlet of the float tank and flows through a pressure reduction valve just as it enters the inlet of the float tank, which results in the air being released in the form of tiny bubbles. Bubbles form at nucleation sites on the surface of the suspended particles, adhering to the particles. As more bubbles form, the lift from the bubbles eventually overcomes the force of gravity. This causes the suspended matter to float to the surface where it forms a froth layer which is then removed by a skimmer. The froth-free water exits the float tank as the clarified effluent from the DAF unit.
Target Impurities :-
- Emulsified Oil, TSS
Advantages :-
- Very Low Retention Time 3-4 minutes
- Small footprint
- Easy to install
- Low chemical consumption
- Very low startup time
- Easy to relocate
- Pre-fabricated unit
- Very low civil cost
- Automatic operation