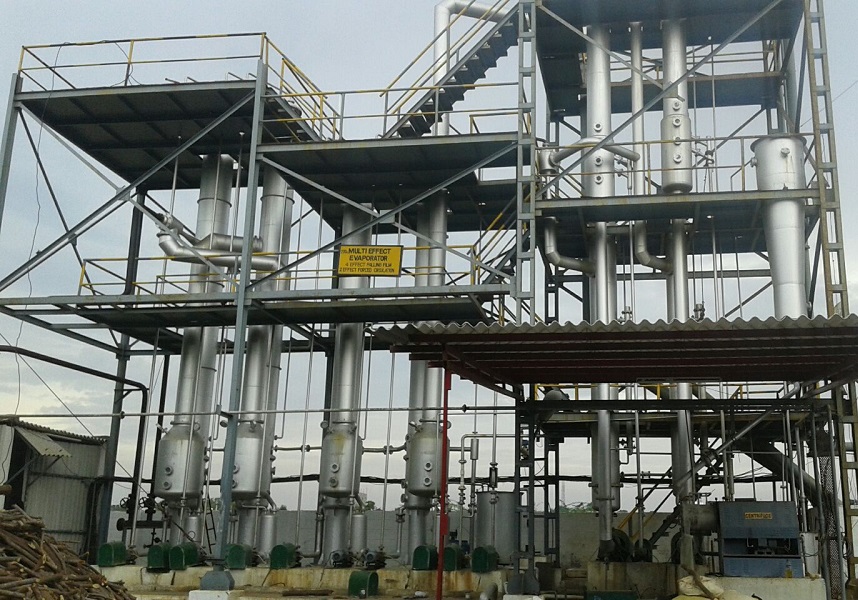
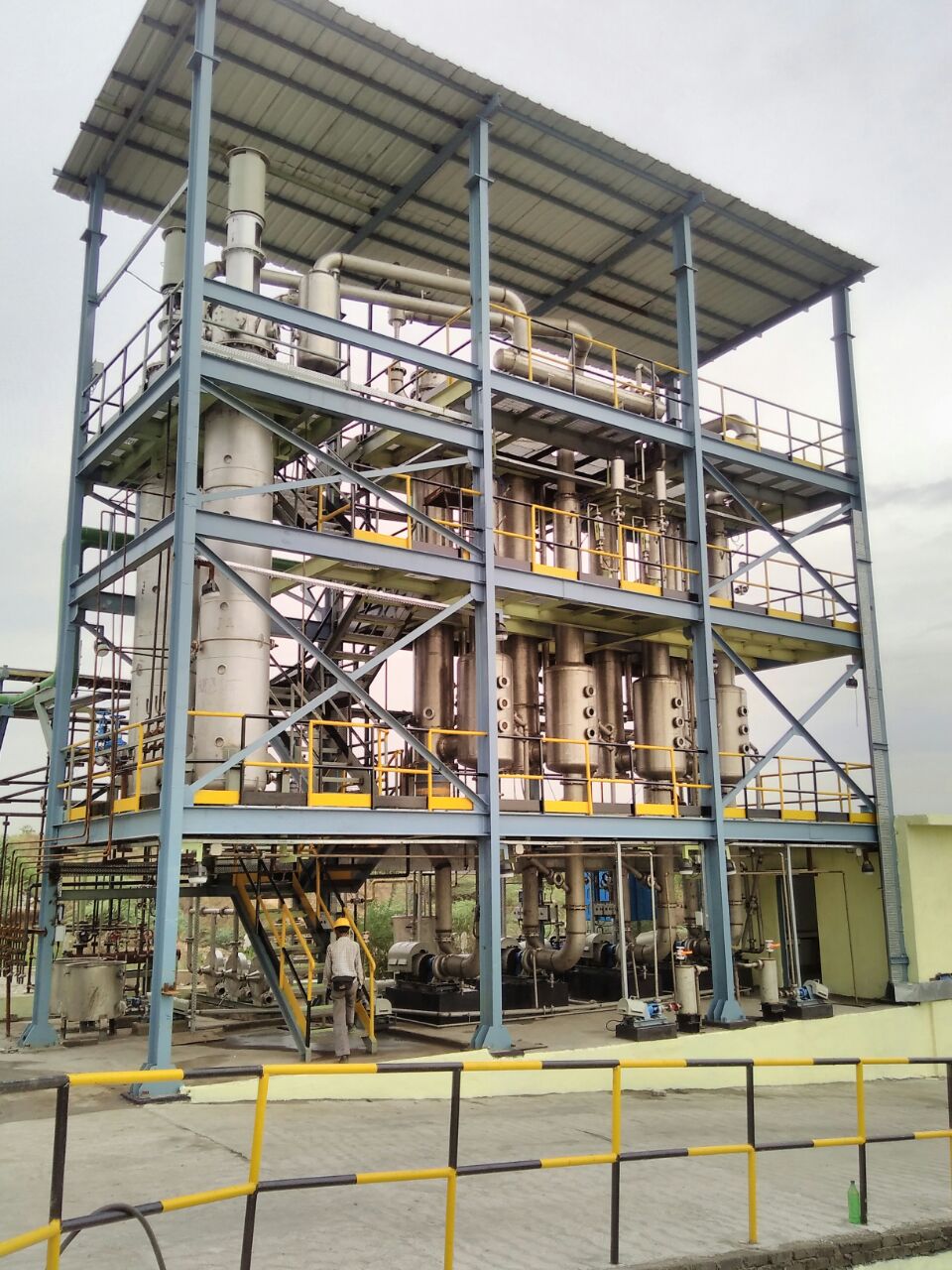
Multi Effect Evaporator (MEE)
MEE is an unit operation involves the stage wise evaporation of the water from any solution/effluent to achieve necessary final concentration.

Process Description :-
Multi effect evaporator is the most efficient and successful conventional evaporation method to achieve a complete zero-liquid discharge for any type of industrial effluent.
Prior to start evaporation process first cooling water circulation is started and generation of appropriate vacuum is being maintain by the vacuum pump, the purpose of the vacuum is to lower down the boiling point of the solution
Through feed pump the feed from the feed tank enters into the shell and tube heat exchanger called calandria by passing through the preheater.
Preheaters are used to exchange the sensible heat of condensate water generated during evaporation process to increase the initial temperature of the incoming feed, simultaneously decreasing the temperature of the condensate water which leads to decrease in the total energy requirement for the entire system
From the preheater effluent goes to the recirculation line of calandria-1 and enter into tubes of the bottom part of the calandria by the force provided by recirculation pump.
Feed passes through shell and tube heat exchanger in the tubes.
To start the evaporation process external steam is being provided to the shell side of the calandria for heating of the tubes.
Due to conductive heat transfer, steam passes its latent heat to effluent and evaporation of water from the effluent takes place. A water-vapor mixture is being generated which goes to Vapor-Liquid Separator called VLS.
In VLS, vapor is separated from water vapor mixture by means of gravity.
While the concentrated liquid is recirculated in the calandria by a recirculation pump.
Now the pure water vapor from VLS is either condensed in condenser or will be used as a heating medium in subsequent effect
This is the simple process of Single effect which uses 1 kg of steam to evaporate the 1 kg of water.
To increase steam economy, we can add 2nd effect, 3rd effect and up to 6 effect and so on.
The vapor of the 1st effect is used as a Heating Source for the 2nd effect and so on up to designed effect. thus, similarly vapor form the intial effect used as a heating medium for the further effect.
Thus, there is no steam is required individual effect except for the 1st effect.
To maintain the proper flow of vapor As we move further in the effects temperature and pressure are in decreasing manner.
Steam Economy statastics:
MEE principle can be continued over further effects to save even more energy.
|
Live Steam |
Amount of Water To Be Evaporated |
Energy Consumption |
|
|
Single Effect Plant |
1 kg |
1 kg |
100 % |
|
Two Effect Plant |
1 kg |
2 kg |
50 % |
|
Three Effect Plant |
1 kg |
3 kg |
33 % |
|
Four Effect Plant |
1 kg |
4 kg |
25 % |
|
Five Effect Plant |
1 kg |
5 kg |
20 % |
This way, by adding no. of effects in the system we can increase the steam economy which leads to overall reduction in steam consumption and boiler capacity and thus in overall reduction in the operating cost of Zero Liquid Discharge.
From the bottom of the last effect, reject of the MEE at a certain concentration, goes to ATFD for final solid liquid separation, and thus achieving true mean of Zero Liquid Discharge.
Advantages :-
- Maximize the steam economy
- Reduce energy requirement to run Zero Liquid Discharge system
- Provision of High Heat Transfer area
- Sustainable and Successful Conventional method for ZLD
Application :-
Zero Liquid Discharge
Waste water treatment
Salt recovery
Caustic recovery
Product concentration